Contents
function filterComparison()
Create real data
Create some real data points(1000points)

sigmax = 5;
sigmay = 3;
rx = randn(1000, 1)*sigmax;
ry = randn(1000, 1)*sigmay;
figure(001);
plot(rx, ry, 'r.');
xlabel('x');
ylabel('y');
axis([-15 15 -15 15]);
[x, P] = MLEnPlot(rx, ry);


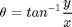
figure(002);
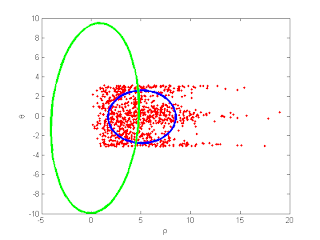
rho = sqrt(rx.^2 + ry.^2);
theta = atan2(ry, rx);
plot(rho, theta, 'r.');
xlabel('\rho');
ylabel('\theta');
MLEnPlot(rho, theta);
fprintf('press any key to continue...\n');
pause;
press any key to continue...

Extended Kalman Filter
Find out jacobian matrix when it transformed by non-linear state transition matrix.
![$$J = \left[\begin{array}{cc} \frac{\partial r}{\partial x} & \frac{\partial r}
{\partial y} \\ \frac{\partial \theta}{\partial x} & \frac{\partial
\theta}{\partial y} \end{array}\right]$$](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEidMCLowrdRWWA3hvetRFLeI2MiKMm6yPLdtgUc5jibvGy3Cnv2T9MIS8YeuMHfInE8ZVA5caXIZgUHkm2s1m-7OPQx4f9JOVr2qZYdNN3FisbeLw-eHdIqkqzTzC0Oh6fT47y7KeSLSdXq/s1600/filterComparison_eq58272.png)
Now, prediction of covariance matrix at the pridiction step

q = x(1).^2 + x(2).^2;
J = [x(1)/sqrt(q) x(2)/sqrt(q); -x(2)/q x(1)/q];
xekf = [sqrt(x(1).^2 + x(2).^2) atan2(x(2), x(1))];
Pekf = J*P*J';
e = make_covariance_ellipses(xekf, Pekf);
hold on; plot(e(1, :), e(2, :), 'g-' , 'LineWidth', 3); hold off;
fprintf('press any key to continue...\n');
pause;
press any key to continue...
Unscented Kalman Filter
Set up some values
D = length(x);
N = D*2 + 1;
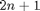
samples are should be generated.
scale = 3;
kappa = scale-D;
Ps = chol(P)' * sqrt(scale);
ss = [x', repvec(x',D)+Ps, repvec(x',D)-Ps];

rho = sqrt(ss(1, :).^2 + ss(2, :).^2);
theta = atan2(ss(2, :), ss(1, :));
x = [rho; theta];
idx = 2:N;
xukf = (2*kappa*x(:,1) + sum(x(:,idx),2)) / (2*scale);
diff = x - repvec(xukf,N);
Pukf = (2*kappa*diff(:,1)*diff(:,1)' + diff(:,idx)*diff(:,idx)') / (2*scale);
e = make_covariance_ellipses(xukf, Pukf);
hold on; plot(e(1, :), e(2, :), 'k-' , 'LineWidth', 3); hold off;

end
function [x, P] = MLEnPlot(x, y)
phatx = mle(x);
phaty = mle(y);
x = [phatx(1) phaty(1)];
P = [phatx(2) 0; 0 phaty(2)];
e = make_covariance_ellipses(x, P);
hold on; plot(e(1, :), e(2, :), 'b-' , 'LineWidth', 3); hold off;
end

from timbailey's matlab utility
function p= make_covariance_ellipses(x,P)
N= 60;
inc= 2*pi/N;
phi= 0:inc:2*pi;
lenx= length(x);
lenf= (lenx-3)/2;
p= zeros (2,(lenf+1)*(N+2));
ii=1:N+2;
p(:,ii)= make_ellipse(x(1:2), P(1:2,1:2), 2, phi);
ctr= N+3;
for i=1:lenf
ii= ctr:(ctr+N+1);
jj= 2+2*i; jj= jj:jj+1;
p(:,ii)= make_ellipse(x(jj), P(jj,jj), 2, phi);
ctr= ctr+N+2;
end
end
function p= make_ellipse(x,P,s, phi)
r= sqrtm(P);
a= s*r*[cos(phi); sin(phi)];
p(2,:)= [a(2,:)+x(2) NaN];
p(1,:)= [a(1,:)+x(1) NaN];
end
function x = repvec(x,N)
x = x(:, ones(1,N));
end








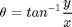

![$$J = \left[\begin{array}{cc} \frac{\partial r}{\partial x} & \frac{\partial r}
{\partial y} \\ \frac{\partial \theta}{\partial x} & \frac{\partial
\theta}{\partial y} \end{array}\right]$$](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEidMCLowrdRWWA3hvetRFLeI2MiKMm6yPLdtgUc5jibvGy3Cnv2T9MIS8YeuMHfInE8ZVA5caXIZgUHkm2s1m-7OPQx4f9JOVr2qZYdNN3FisbeLw-eHdIqkqzTzC0Oh6fT47y7KeSLSdXq/s1600/filterComparison_eq58272.png)


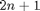 samples are should be generated.
samples are should be generated.

